
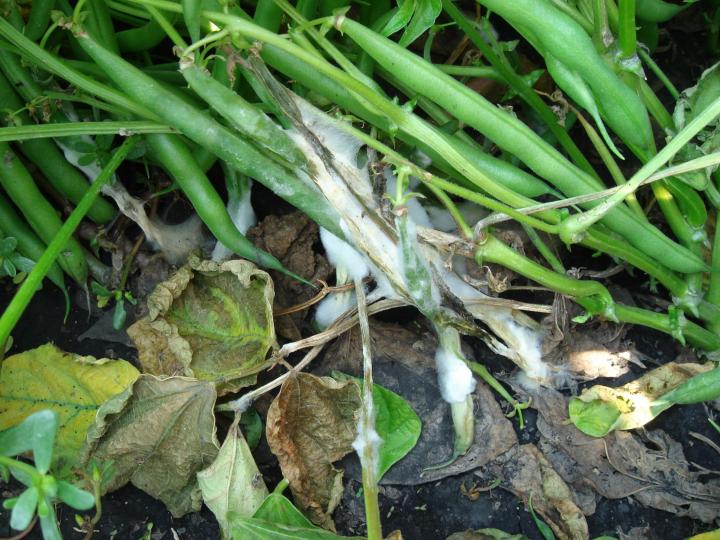
How to Identify and Control White Mold
ADVERTISEMENT
What do I do when this happens to my house plants?
I put them outside, weather permitting, in spring and bring them back in when the weather begins to get cooler. (Fall)
Thank you, Mary Formichelli
One method that will work to delay, if not offset permanent damage to the plants, or end in their death, is to cleanse the contaminated whitened areas thoroughly with a white vinegar base using a new sponge or soft rag. If the discretion returns you can try altering your watering method or habits (i.e. using a bulb or ice cubes instead of spray bottle, or integrating a watering routine three times weekly as to every other day, etc). Then also cleanse the affected areas again so that the contamination doesn't spread among the leaves or to the other plants. Good luck!
Thanks For sharing this information. It’s Nice..!!!
This is a great post. I like this topic.
Hi, is it safe to eat the veggies in garden with white mold? If not, should I get rid of the dirt and start over? What do I do?? Thx









Comments