
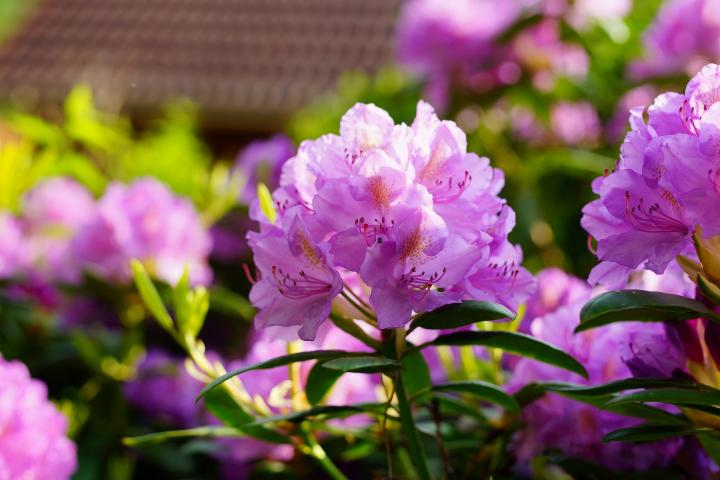
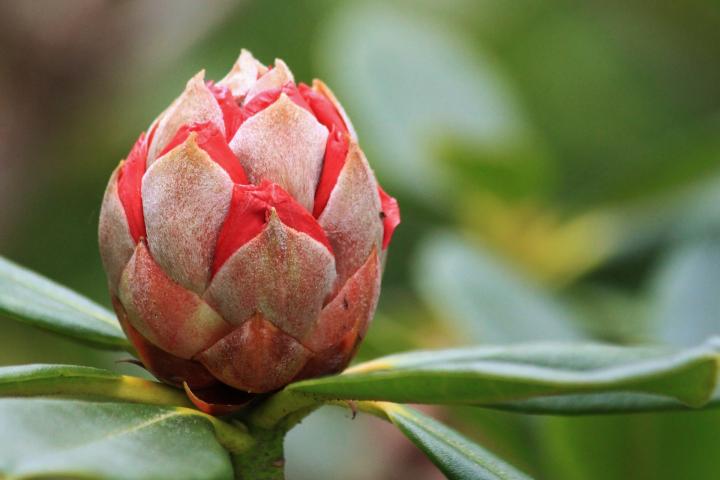
How to Plant, Grow, and Care for Rhododendron and Azalea Shrubs
ADVERTISEMENT
Can my fairly shaded rhododendrons survive in the whole month of September in Michigan without watering?
It really depends on how dry or wet your part of the state has been and is expected to be. If you get plenty of rain in August and September, and temperatures cool off, then the plants should be fine, assuming they are planted in the ground. If they’re in containers, they will likely need some extra watering if conditions are dry.
I'm new to Rhododendrons, ibought 2 beautiful 'Polarnacht' yesterday but how do I find out what zone I'm in to give my plants a chance to survive. Thank you
Almanac has this available on their site, then all you need to do is input your zipcode. I also like to look up plantmaps.com . If your city has more than one plant hardiness zone, this site shows a map and you'll be able to easily locate exactly which zone you're in. We live alongside a mountain range and have three different plant hardiness zones in our city, so this helps a lot as to which one pertains to us.
a series of sucker-like, tall sprouts have developed. Could I have pruned them incorrectly?
Should I snip them off sometime?










Comments