
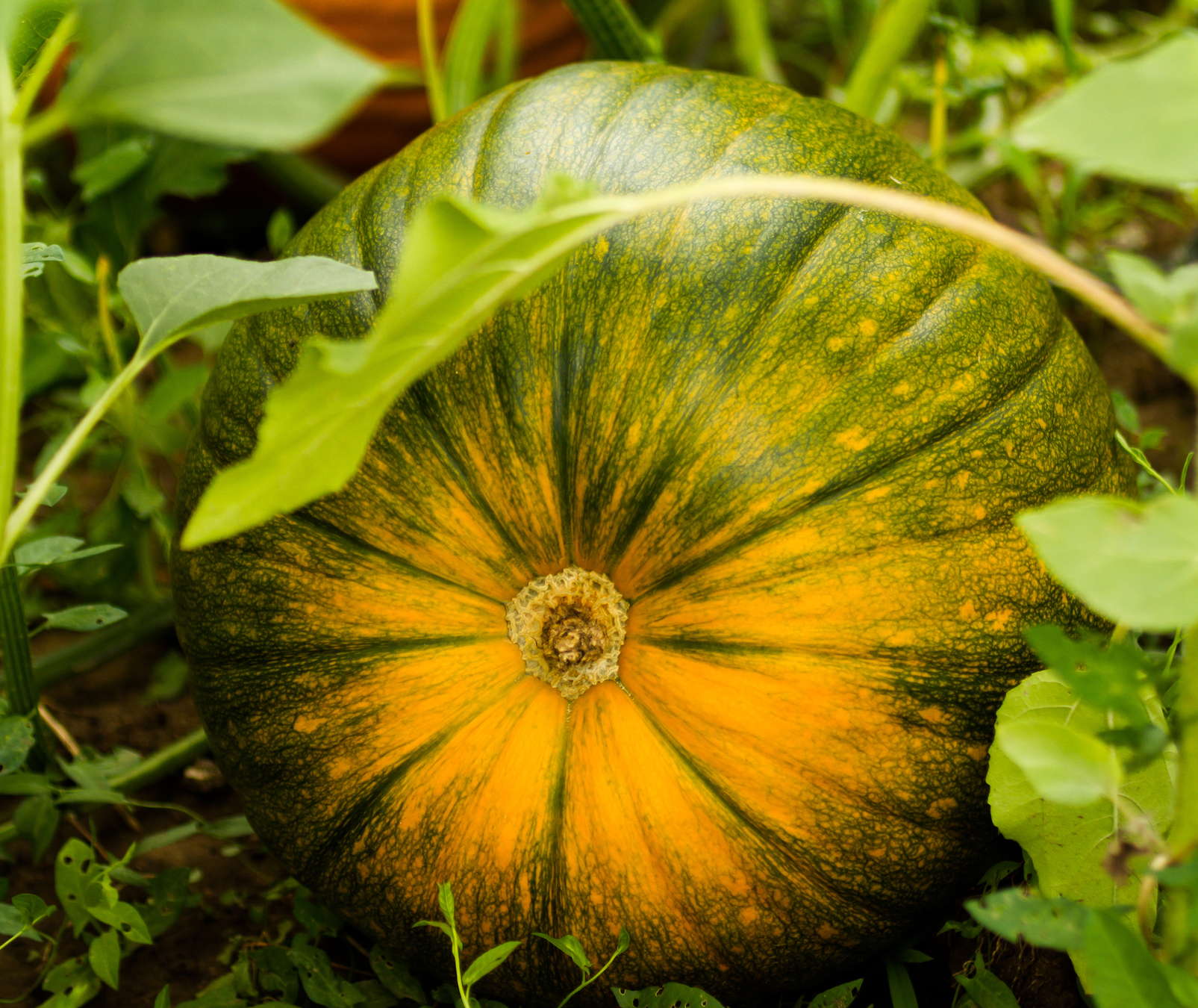
Pumpkin Planting & Growing | Learn How Pumpkins Grow
- See how to clean a pumpkin for cooking.
- Don’t forget about the seeds! Roast them with salt or cinnamon for a tasty treat.
ADVERTISEMENT
Every one is sharing information, that’s truly good, keep up writing.
Thanks for sharing this quality information with us. I like this information.
vector art services
I have a pumpkin that’s a year old! Kept it inside the house during the winter months and then put it outside this summer!!
It’s still in great shape, solid and heavy!! How can this be???
Color has changed somewhat going to a dark green!
Thanks for the great info about pumpkin growing! I have an issue with two pumpkin varieties I’m growing in different raised beds, I’m wondering if you might have any advice. I’ve been waiting for the female flowers to come up. I finally saw them budding up on my vines but after a few days, they turn yellow and pop off the vine. Am I not fertilizing enough maybe? Thanks again!
Hi, Wylie, Lots of things can cause lack of pollination. Some of the most common causes are lack of pollinators; weather, specifically extreme heat or cold temps. Varieties differ in their reaction to temp changes. Nitrogen levels in the soil can also affect fruit set. Excess nitrogen results in vigorous vine growth and delays flowering. You might do a soil test to assess its composition. We hope this helps!









Comments