
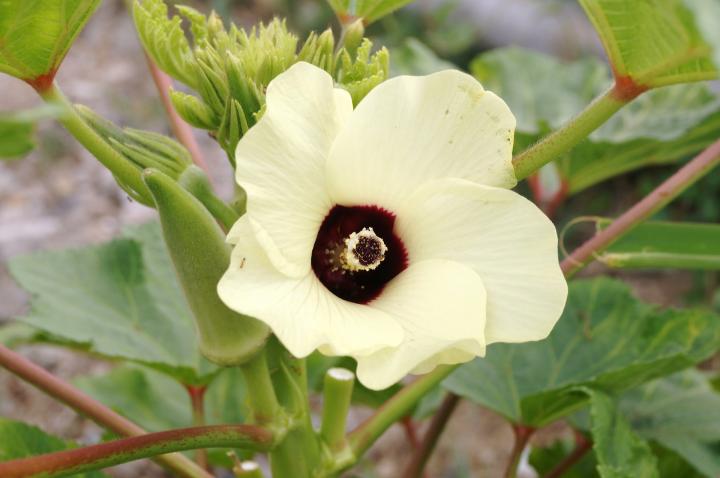
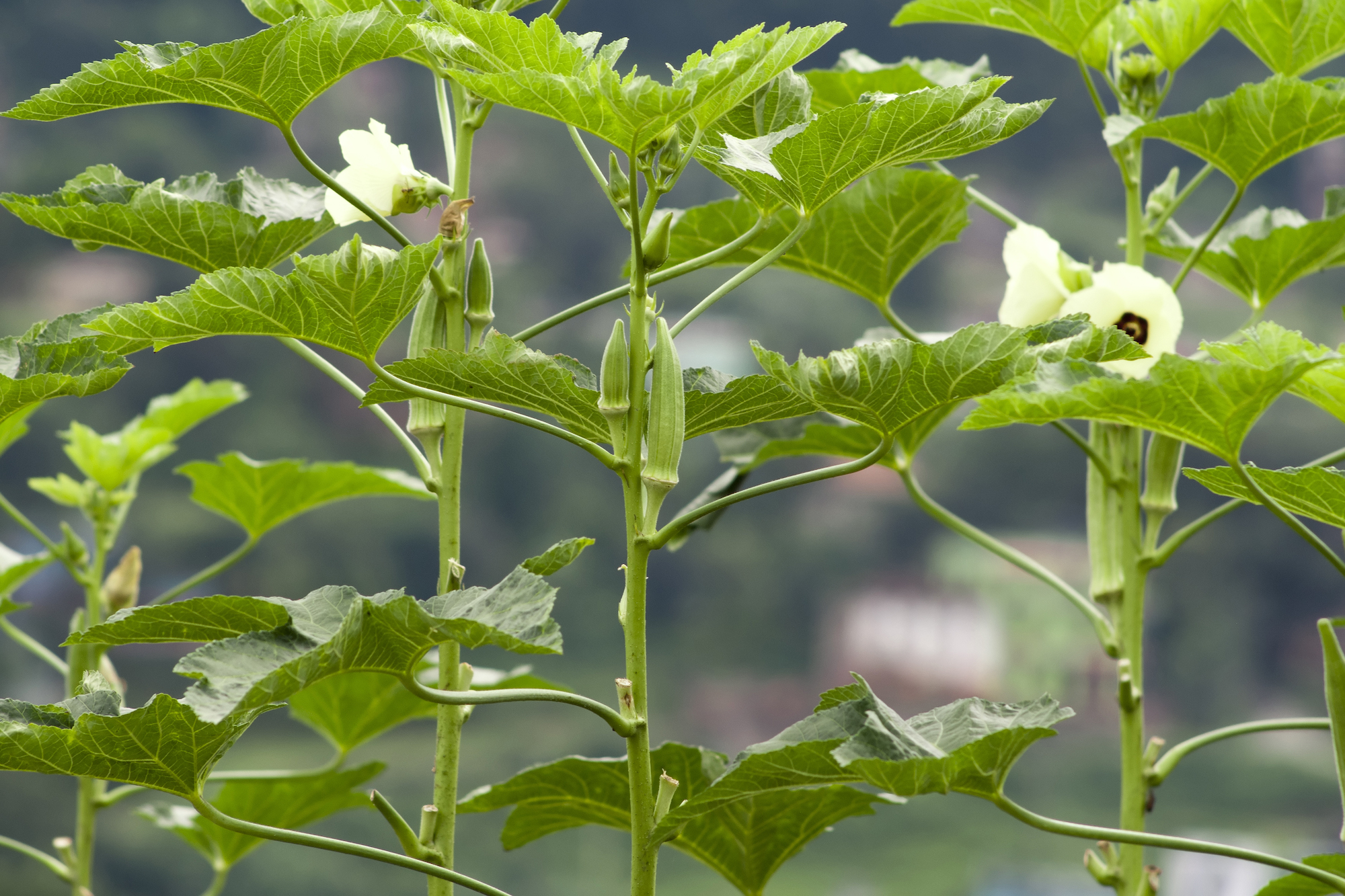
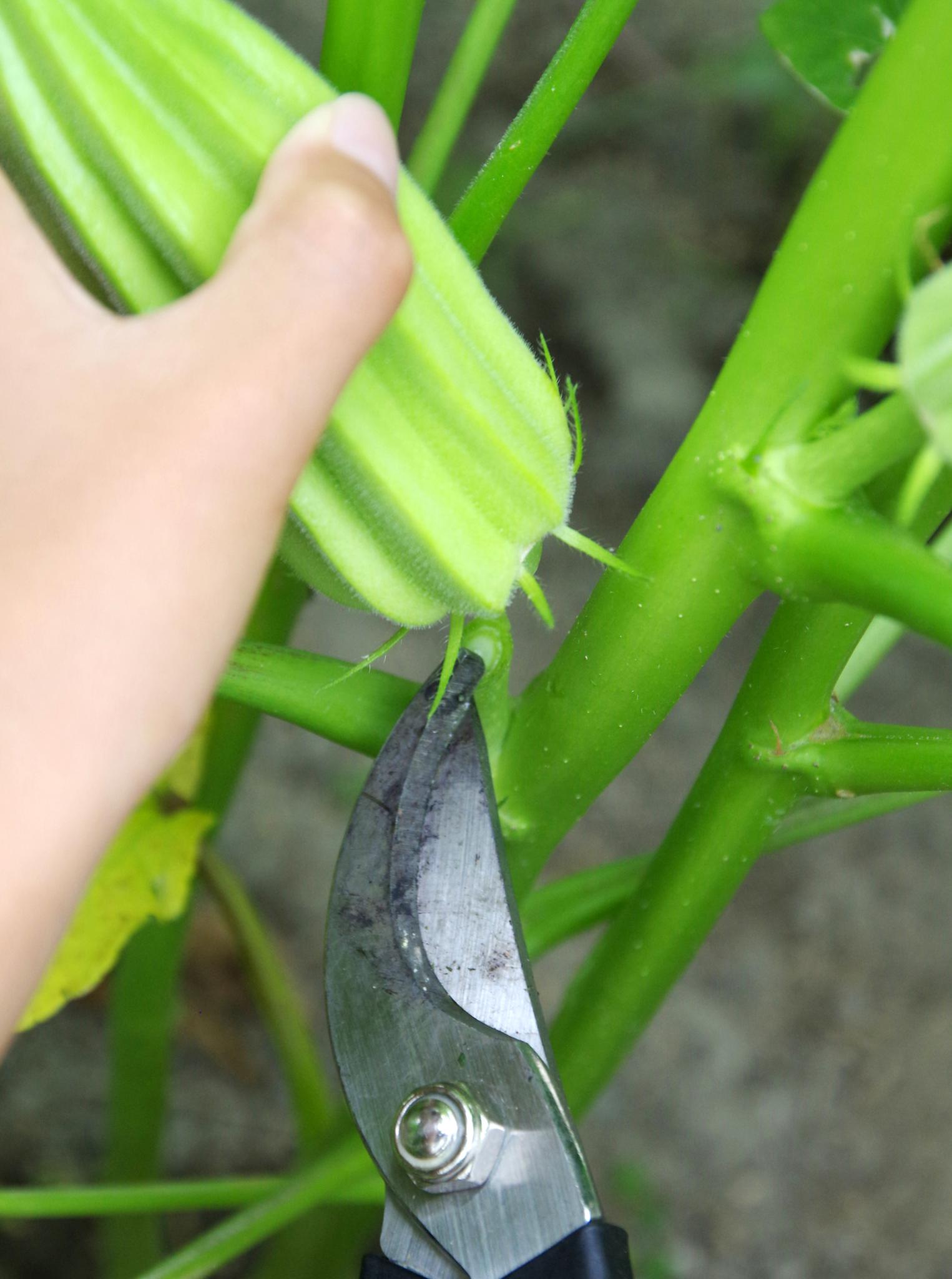
Planting, Growing, and Harvesting Okra
Okra can be consumed in a number of ways—breaded and deep-fried, pickled, stewed, in Indian cuisine, and even raw in the field! Of course, the most famous okra dish is probably gumbo.
For a nice stewy dish, simmer fresh tomatoes and onions and perhaps some pre-fried bacon pieces. Add chopped okra. On the stove, cook for 25 minutes and the soft insides of okra will help create a nice thick savory broth to serve over rice.
Or, try roasting okra bring out its natural nuttiness. Just remove the cap and split lengthwise, and roast on a baking sheet for 25 minutes; we cover with aluminum foil for the first half of cooking.
ADVERTISEMENT
My Mother tried to cook some okra years ago and it turned out SLIMMY! When I grew up and I tried cooking it, it too turned out SLIMMY!!!! I would never try it again. How they eat it in the south I could never figure out.
Well best practice is to add a little lemon or lime juice. myself I saute` tomatoes [with onions if you like] and add cut okra. this makes a good side dish just like that or proceed to make stew or gumbo. canning or pickled okra is good and results in crispy pieces [uncut], goes well in a nice green salad also.
Try steaming it in a basket until it's bright green. Or fry it. Cut each pod into 1/4"-1/2" lengths, coat with your favorite breading mix a fry in a pan on medium heat until golden brown.
I live in North Central Florida and my okra plants have been doing great all along, except for a about a month ago, I started cutting off the dry leaves and now the trees have stopped and or in some cases not producing as much as before. Thanks
I live in south Georgia my orka plants are just starting to bloom but the bloom is turning brown and falling off. What do I need to do











Comments