
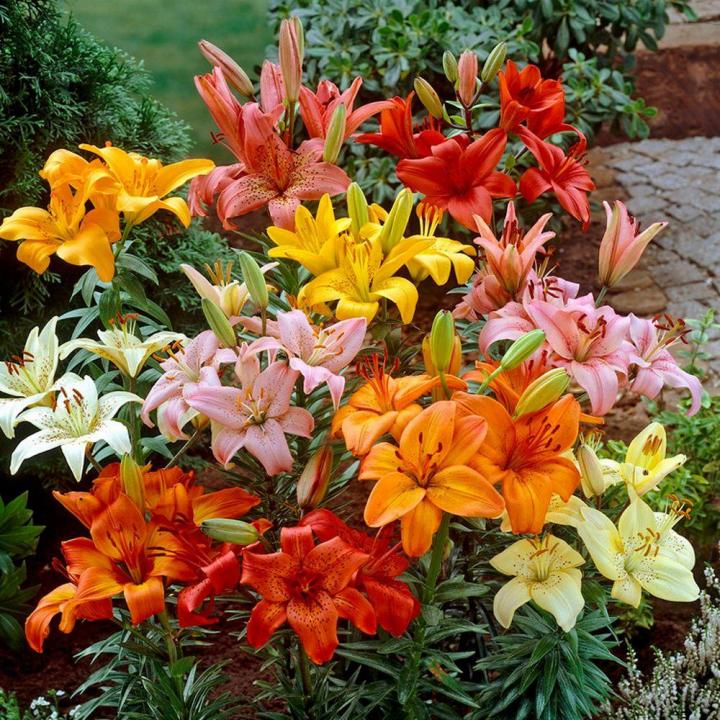
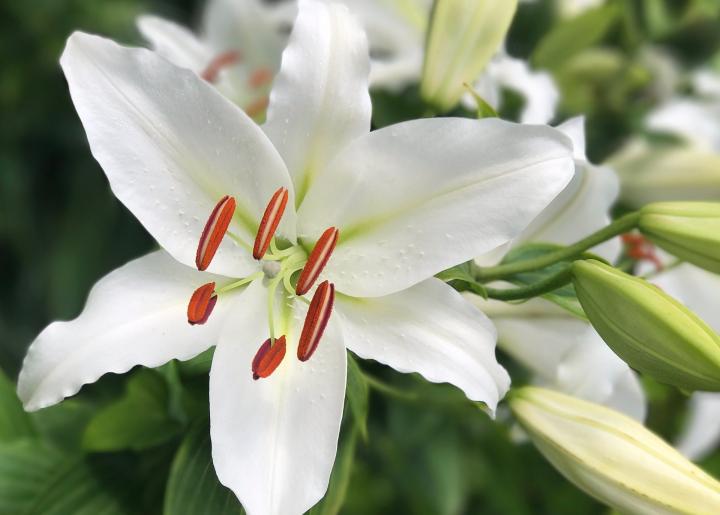
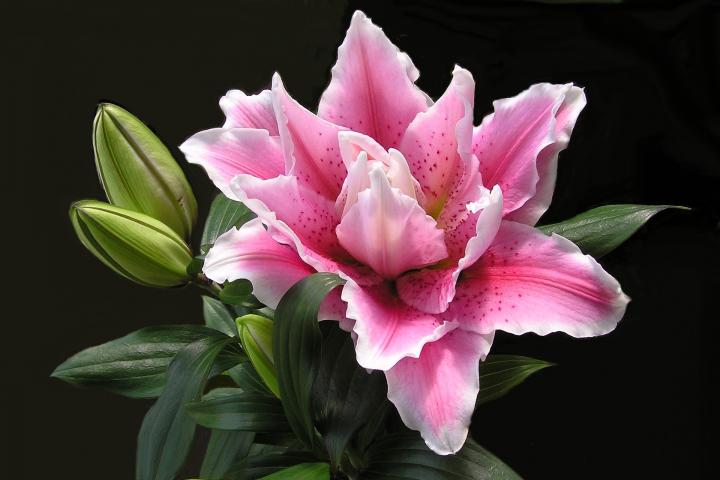
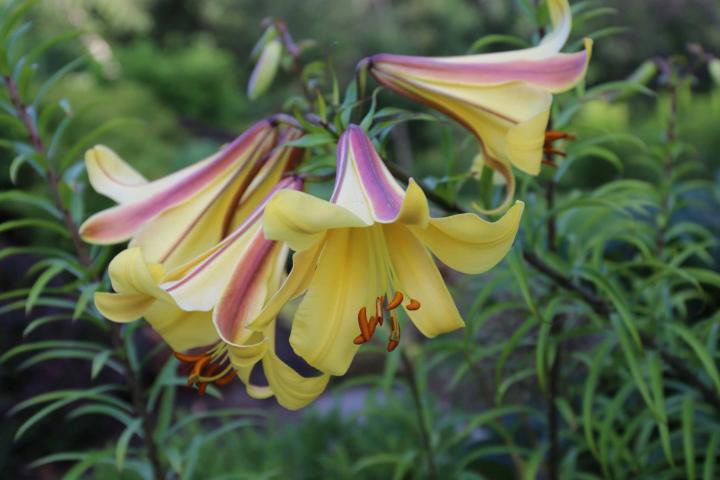
How to Plant, Grow, and Care for Lilies
ADVERTISEMENT
I didn't find this question anywhere: I ordered lily bulbs and received them with sprouts. Should I go ahead and plant them even though the are trying to grow in the fall?
Got asian lilies as a gift. Blooms fell off 3 weeks ago. ? do I let it renew blooms w/o help or do I cut the old stems back or any advice. Thanx Joe B
Joe, I think this is what you are looking for; this and more appears on this page above:
- Lilies do not bloom more than once per season, but you can remove the faded flowers so that the plants don’t waste energy making seeds.
- After the lily blooms, you can also remove just the stem itself. However, do NOT remove leaves until they have died down and turned brown in fall. It’s very important not to cut back the leaves until the end of their season because hey help provide nourishment to the bulb for next season’s blooms.
- Cut down the dead stalks in the late fall or early spring.
I know bugs go after my rose bushes I use a mixture of soap and water. I wonder if that will work for Lily’s my daughter bought me two plants for Mother’s Day. I am working out where to plant them.
I too am infested with red lily beetles but I refuse to give up. I love my lilies too much. I have Oriental, Asiatic, Easter, and my favorite, Tiger lilies. I'm retired now (Yeah!) so at least 2 or 3 times a day I'm out with my flowers squishing those critters with my bare fingers. I used to hate killing things, (I know pesticides won't work), but to save my lilies I will do it. I also squish those dastardly gross brown globs of gook on the leaves, too. It's a challenge, but my lilies are absolutely gorgeous. I'm still winning!!!












Comments