Kombucha tea is a popular fermented drink with a unique, tangy flavor. Did you know that you can make it yourself? Learn how with our recipe!
Advertisement
What is Kombucha Tea?
Kombucha is a delicious fermented drink that’s perfect for a warm summer day. At its heart is a live bacterial-fungal culture called a SCOBY (Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeasts), sometimes referred to as a “mother.” The mother looks like a circular, flat jellyfish and is made of good bacteria—probiotics that can help to keep your stomach’s microorganisms in balance.
Combining the sweet and sour flavors of sparkling cider, apple cider vinegar, and mild white wine, kombucha is made from a mixture of tea, sugar, and live culture (scoby). Green and black teas are the most commonly used, but don’t feel limited by those options. You can make kombucha from almost any kind of tea, but avoid any with artificial flavoring—the added ingredients will inhibit or stop the bacteria’s growth.
A by-product of the fermentation process is a small amount of alcohol, the majority of which is converted into organic acids. At most there will be 1 to 1.5 percent of alcohol left in a batch of finished kombucha.
What are the Health Benefits of Kombucha?
During fermentation, kombucha culture breaks down sugar to produce a range of organic acids, vitamins, enzymes, and minerals, all of which our bodies use to maintain our health.
Kombucha helps with digestion problems, preventing candida yeast overgrowth in the gut and stomach (though you should avoid drinking kombucha if you already have candida overgrowth). Kombucha is also said to inhibit harmful bacteria, detoxify the liver, promote blood circulation, and fight arthritis by creating glucosamine, a key component in the makeup of joint fluid and cartilage.
Kombucha Recipe
Want to make your own kombucha? For your first batch you will need the following:
- 1 half-gallon Mason jar
- 6 cups boiled water
- 4 bags of tea
- ¾ cup sugar (any type will do; we used an organic cane sugar in this recipe)
- 1 ½ cups starter kombucha (starter culture)
Note: The best place to look for your starter culture is a health food or natural foods store with kombucha on tap. Their kombucha will usually still have an active culture in the tank and be able to grow a new scoby. If you’re unsure, look up the website of the brewer or ask the store purchaser. Avoid buying pre-bottled kombucha because it is flash frozen to prevent the transmission of dangerous bacteria, which eliminates the live culture you need.
Before Beginning …
Sterilize everything during the brewing process to keep the kombucha from growing mold. You only have to worry about mold during the first three days, when the pH of the tea is still above 2.5-3. Once it reaches those levels of acidity, your kombucha is safe. To identify any mold, look for blue or black fuzzy spots on top of the scoby—it looks like the kind of mold you would find on fruit. If you’re not sure, play it safe by throwing the mother away and starting again from scratch. Just like with moldy food, drinking kombucha from an infected batch can make you sick. Don’t risk it.
Instructions
-
Using boiling water, sterilize all of your measuring cups, the Mason jar, and any spoons used for stirring.
-
Boil 6 cups of water, pouring it into the jar. Add 4 tea bags. Let them steep for 8-10 minutes before removing.
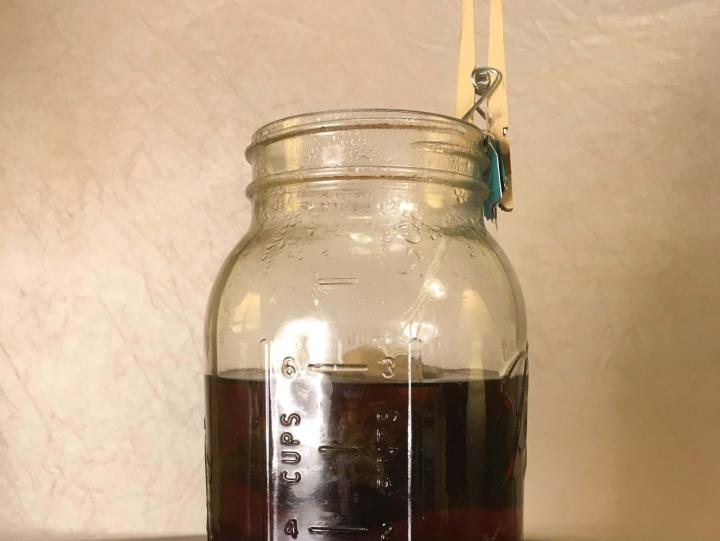 Steep the tea bags in the boiled water for approximately 10 minutes.
Steep the tea bags in the boiled water for approximately 10 minutes.
-
Add sugar to the hot tea and stir until it dissolves entirely. Let the tea cool to room temperature (~72°F). If the tea is too hot, it will kill your live culture in the next step.
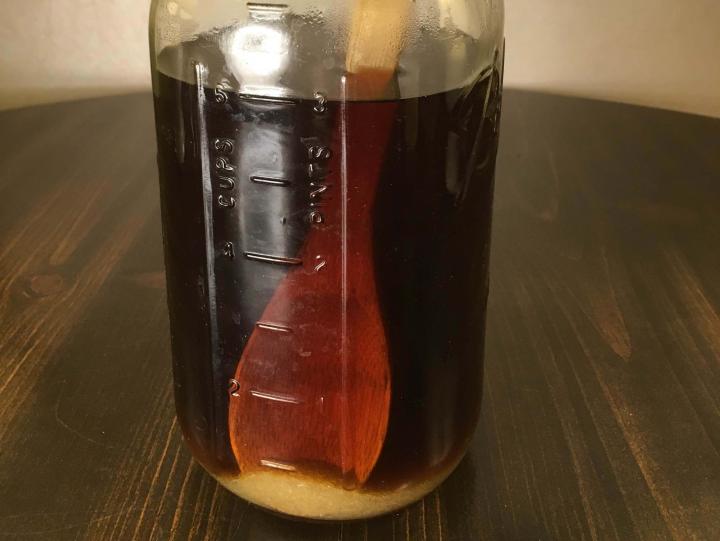 Stir the sugar into the warmed tea until it is fully dissolved.
Stir the sugar into the warmed tea until it is fully dissolved.
-
Pour starter kombucha into the cooled sweet tea and stir gently. Cover the top of the jar with a clean cloth or towel and set it in a dark place, such as a kitchen cupboard. Let the brew ferment for 7 days. The symbiotic culture thrives at about 80°F, though it will still work at temperatures ranging from 70° to 90°F.
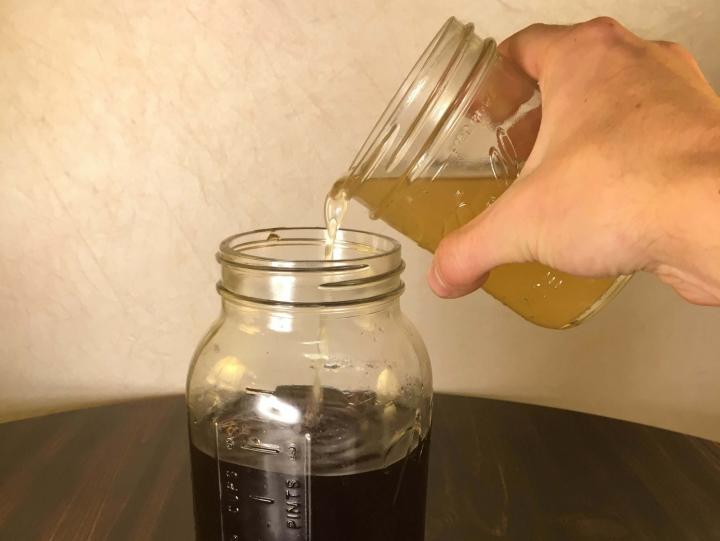 Pour the starter kombucha into the cooled sweet tea.
Pour the starter kombucha into the cooled sweet tea.
-
Once the tea has fermented, remove the jar from the cupboard. There should be a thin gelatinous layer on top of the tea in the jar—this is the kombucha scoby! It should be opaque, yellow tinged, and gray-white.
-
Brew a new batch of tea and sugar in another mason jar. Sterilize a plate and your hand, or use sterile gloves, and gently scoop the mother out of the brew, placing it on the plate. Take a cup of kombucha from the brew you just made and pour it into the new one. Gently pick up and slip your mother into the new batch so it floats on top.
-
Make sure you keep the orientation the same. The top of your scoby is bacteria which likes the open air while the bottom is yeast, which likes to be submerged. Neither will do well if their environment is switched.
-
Once the scoby is grown, you do not have to follow this recipe’s exact measurements, only this ratio: 4 cups tea – ½ cup sugar – 1 cup starter kombucha. A scoby can make any size batch.
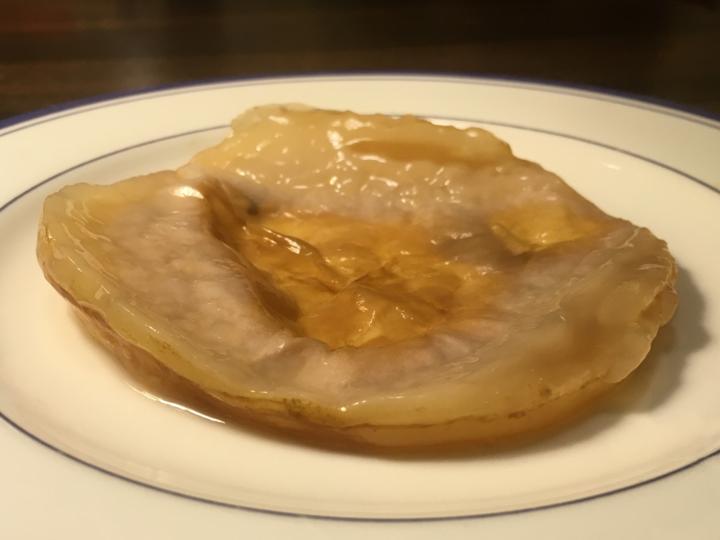 A mature homegrown scoby
A mature homegrown scoby
-
Screw the lid onto the jar of the old batch of kombucha. The tea is ready to drink—if you enjoy a little carbonation, then leave it for another 3 to 7 days on a counter out of direct sunlight to further ferment. Keep it in the same temperature range as during the first fermentation. You don’t need to keep it in the dark, but avoid direct sunlight. Unscrew the lid once or twice a day to release the buildup of pressure, which is also called ‘burping’. If you don’t burp the jar, the pressure could build up and burst the jar.
- Once the second week is up, or when the tea has enough carbonation to your liking, put the jar in the fridge to prevent the live culture from fermenting any more. In a cold environment, the bacteria and yeast will slow their processes.
-
Time to drink your kombucha! If you’re not planning on drinking your entire batch right away, try pouring it into screw-on–top glass bottles or re-sealable wine bottles. There may be some sediment in the liquid—don’t worry; this is just leftover yeast from the fermentation process. If you don’t like the sediment, you can use a filter or a food grade plastic hose to avoid siphoning the yeast.
Future Kombucha Batches
For future batches of kombucha, your scoby will create a baby mother underneath itself, submerged in the tea. If there is none, don’t be discouraged. Your mother needs to grow before it can produce an offspring. Give it a few cycles to thicken.
When you do find a baby growing, you have a few options. You can leave it to bolster the size of your existing mother, separate them and start a second batch with a different kind of tea, or give it to a friend to jump start their own first brew!
Have you ever made kombucha before? Let us know in the comments!
More Traditional Drinks
Kombucha not quite your cup of tea? Try one of these other traditional homemade drinks:


 Steep the tea bags in the boiled water for approximately 10 minutes.
Steep the tea bags in the boiled water for approximately 10 minutes. Stir the sugar into the warmed tea until it is fully dissolved.
Stir the sugar into the warmed tea until it is fully dissolved. Pour the starter kombucha into the cooled sweet tea.
Pour the starter kombucha into the cooled sweet tea. A mature homegrown scoby
A mature homegrown scoby







Comments