
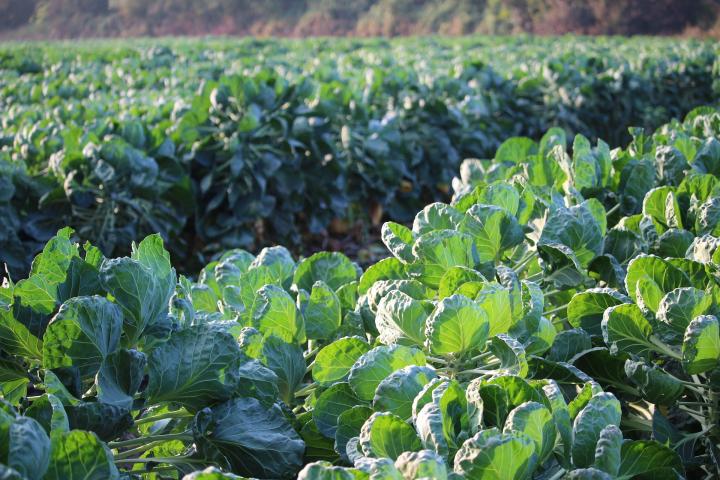
Planting, Growing, and Harvesting Brussels Sprouts
We prefer roasting sprouts—they have a lovely carmelized flavor!
ADVERTISEMENT
Hi All,
This is my first year growing brussel sprouts. Actually did it on a whim. What a surprise I was in for!
The seller I bought the house from in 2020, were not Gardner’s, but I found raised beds on the side of the house. (3) 5X8’. I found everything in there from old dish towels, broken and rusted steel pipes, an old broken weed eater, plastic bags… you name it.
When the Brussels Sprout package said to plant of thin to 12-24”, they mean it!
Next year I’ll stretch it out to maybe 30-35 inches.
I removed the garbage, weeds and everything else.
I put in 3 bags of commercial compost, mixed it into the existing soil, and experimented.
On one side of the bed I planted carrots, the other side I put in 3 Sprout plants.
3 plants in 8 feet is not enough room. ( Best 60 carrots I’ve every grown!)
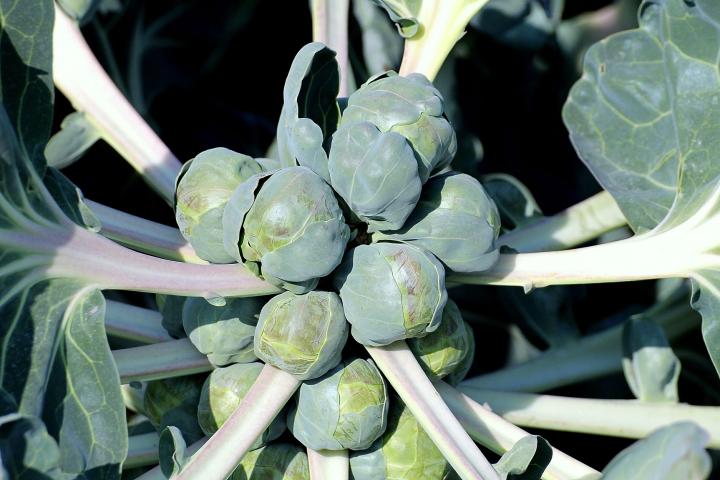
The plants are every bit of 3 feet high and have hundreds of sprouts on each.
One of them, I suppose he felt squished, started growing side shoots next to the ground and those created their own root and are baring sprouts all on their own.
The first frost has come and gone.
I light snow.
So Today I’m going to start harvesting dinner size portions off the main stalk.
We’ll see how it goes.
This was our first year growing brussel sprouts. We kept waiting for them to show up above the plant. We finally realized they were below the large leaves. So funny! We also grow carrots and I can’t believe how delicious they are! Enjoy your gardening.
I planted Brussel Sprouts last summer as an experiment and the plants did not do very well, possibly due to weather condition. Had no sign of sprouts. After the snow melted this spring, I was surprised to see them come alive, specially one particular one that grew very tall within a month and then it flowered. However many plants have started to come out of the stem (which has become quite thick and tough by now). Can I grow them from what looks like new plants? If so, how?
One of these have grown 1 feet tall but again no sign of sprouts formation. Can I relocate it to a more fertile location?
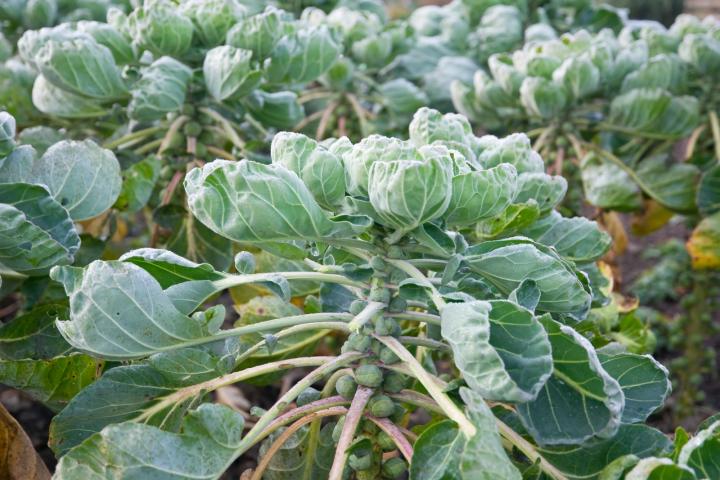
Loads of large leaves , where are the sprouts hiding? Do I trim back any leaves? It is the end of September but no frost yet?
The sprouts appear underneath the leaves—look at the bas of each leaf and a small sprout should be forming.











Comments