
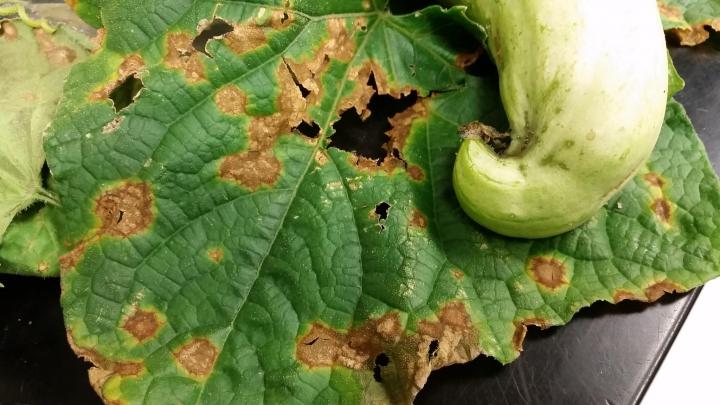
Fungal anthracnose attacks these young grapevine leaves.
How to Identify and Control Anthracnose
ADVERTISEMENT
Will pruning affected trees and destroying the leaves be enough to prevent recurrence? I may missing it, but I don't see any information about how to prevent recurrence in trees? Lots of info on plants, but I don't anything preventative for large trees.
Thanks.
Does additional anthracnose treatments needed every year to large maple trees to prevent initial infection during the first year.
Removing infected leaves can help to stop its spread, but anthracnose can overwinter in twigs or other parts of the tree, so it’s unlikely that you would be able to get rid of it completely. Generally, anthracnose isn’t as big of an issue in trees as it is in smaller plants, so it’s often something that is just tolerated. However, if the tree seems to weaken and have a lot of leaf loss, fungicides can be used. Read more about that here: Anthracnose
I work at TESYD Farms as T.O. and I have noticed that most of the young seedlings have their leaves with many dark spot looking like it has been sprayed with weedicide. Can that be anthracnose?.
I have recently bought a mango tree and it has black regions on my branches.It doesn't seem to be effecting the leaves much yet . I'm not sure if its Anthracnose any help would do. I've also noticed broken leaves I'm not sure if that has anything to do with it.









Comments